Introduction To The Functions Of Battery Management System (BMS)
BMS, namely Battery Management System, has the main function of intelligent management and maintenance of battery cells, preventing overcharging and overdischarging, prolonging battery
life, and real-time monitoring of battery status. Therefore, the requirements for battery system management are as follows:
1. Safety requirements:
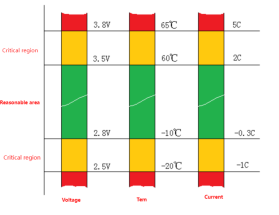
Without a BMS, there would be potential safety hazards such as combustion or explosion. Batteries have certain operating conditions - such as current limit for charging, current limit for discharging, temperature limit for operation, voltage limit for individual cells, etc. The operating conditions of batteries are divided into "reasonable areas" and "critical areas". When the operating conditions of the battery cross the "critical area", the probability of accidents will increase significantly. The BMS needs to take measures to prevent accidents from occurring.
2. Extend battery lifespan.
There are certain operating conditions for batteries. When the battery is operating within the "reasonable range", its lifespan is longer. Entering the "critical range" will significantly reduce the lifespan, and crossing the "critical range" poses safety risks. To increase the battery's lifespan, try to keep the battery operating within the "reasonable range". When the battery exceeds the "reasonable range", an upper-level alarm should be triggered to bring the battery back to the "reasonable range".
3. Increase the effective energy storage of the battery pack.
Each individual battery has limited energy, so most batteries are connected in series for use. The batteries connected in series are called battery strings. Due to the inherent differences among batteries, there are variations in the stored energy. Over-discharge and over-charge are two extremely dangerous states for batteries. During discharge, when a certain battery reaches the discharge limit, even if the other batteries still have energy, discharge cannot continue. Conversely, during charging, when the voltage of a certain battery reaches the upper limit, even if the other batteries are not yet fully charged, charging must be halted. Therefore, discharge is limited by the battery with the lowest voltage in the string, and charging is limited by the battery with the highest voltage. Thus, "effective energy storage" is less than "theoretical energy storage". Without BMS, the energy difference among batteries will increase, and thus "effective energy storage" will decrease. The value of the battery lies in its "effective energy storage". If BMS can inhibit the trend of battery "consistency" deterioration, it means that "effective energy storage" is closer to "theoretical energy storage", and the battery discharge time can be extended.
4. Estimate the remaining battery energy.
Without BMS, it is impossible to know how much remaining energy the battery has, and the remaining energy can predict how many miles the vehicle can still travel.
In general, BMS measures, obtains the battery's operating status, and displays it. In emergency situations, it reminds the user to keep the battery operating within the "reasonable range", thereby extending the battery's lifespan. In dangerous situations, it automatically takes measures to avoid accidents. Additionally, it provides an energy balance function for the battery to increase its "effective energy storage", thereby extending the discharge time.
[Introduction to Battery System Functions]
The BMS battery management system is generally composed of terminal module, core control module, display module and other components:
The terminal module directly interacts with the battery and performs the following functions:
(1) Precise measurement of battery voltage.
(2) Measurement of battery temperature.
(3) Energy balancing.
(4) Thermal management.
(5) CAN communication.
The battery core control module is the core of the BMS system and mainly performs the following functions:
(1) Voltage/current measurement.
(2) Insulation resistance measurement.
(3) SOC calculation.
(4) Data analysis and graded alarm.
(5) Protection control.
(6) CAN communication.
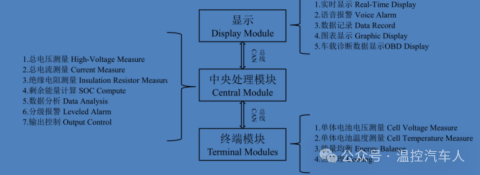
The display module mainly interacts with the large-screen display interface and mainly accomplishes the following functions:
(1) Routine data collection.
(2) Real-time data display.
(3) Voice alarm.
(4) Data recording and chart display.
【Analysis of Battery Management System Function】
1. Single-cell Voltage Measurement
Voltage is one of the most important parameters for characterizing the condition of a battery. On one hand, there is a certain relationship between the battery's charging state (SOC) and voltage. By monitoring the voltage of the battery, one can roughly understand the charging state of the battery:
In the BMS system, the initial function of measuring the cell voltage can be achieved in the following ways: first, by observing the voltage to roughly understand the charging and discharging status of the battery; second, to provide safety protection based on the voltage. The state of the battery is also related to current and temperature. In fact, the functional relationship between different individual batteries is also significantly different. Using multiple parameters to calculate and correct the SOC is more accurate.
2. Temperature
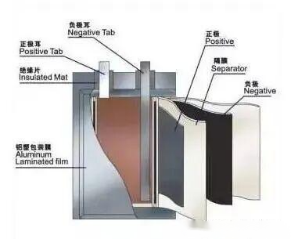
Monitoring and measuring the temperature of the battery is crucial because an increase in temperature poses the risk of combustion and explosion of the battery. There is a plastic separator between the negative electrode material (generally graphite) and the positive electrode material (lithium iron phosphate/ternary lithium). The "separator" blocks direct contact between the positive and negative electrodes but allows lithium ions to pass back and forth through the fine pores on the separator. When the temperature rises to a certain level, the "separator" softens and is easily punctured by the crystalline negative electrode material lithium iron phosphate, causing a short circuit between the positive and negative electrodes and triggering an explosion. The factors causing temperature rise include the internal resistance of the battery and the contact resistance between the external terminal and the wiring connector.
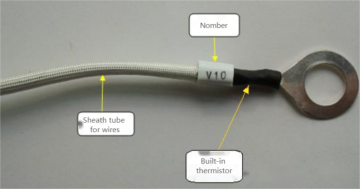
There are two approaches in the market. One is to set a fixed number of temperature probes and distribute them throughout the "battery cluster". The other is to place the probes on the terminals of the voltage collection lines, and monitor and measure the temperature of each battery.
3. Protection Control
Based on the current usage situation, the protection control of BMS should include protection against overcharge, overdischarge, overcurrent, and overheating. The control signals are divided into two paths for overcharge and overdischarge, or they can be combined into a single master control signal.
4. Energy Balance
First, let's understand why energy balance is necessary. There are certain consistency differences between individual batteries and small modules, which arise from factors such as the concentration difference of the negative electrode material, the crystal structure of the negative electrode material, the uneven coating uniformity, the thickness of the separator, and the uniformity of the pores in the separator. New batteries can achieve a high degree of consistency in battery energy through screening (so-called grouping and pairing). However, after several charge and discharge cycles, this consistency no longer exists, manifested as significant differences in the remaining energy between individual cells.
During discharge, when a certain cell reaches the discharge limit, even if other cells still have energy, discharge cannot continue. During charging, when the voltage of a certain cell reaches the upper limit, even if other cells are not yet fully charged, charging must be stopped. Therefore, discharge is limited by the cell with the lowest voltage in the series, and charging is limited by the cell with the highest voltage. There will always be cells that cannot be fully charged, and cells that cannot be fully discharged. This leads to the "effective energy storage" always being lower than the "theoretical maximum energy storage".
Therefore, in order to make the "effective energy storage" reach the "theoretical maximum energy storage", it is necessary to use some means to make the remaining energy of each individual cell tend to be consistent, so that each individual cell discharges and charges basically simultaneously, which is what is called the BMS balance function.

